Web3, также известный как Web 3.0 - это эволюция интернета, которая обещает революционизировать способ взаимодействия и обмена информацией в онлайн-мире. Этот термин означает множество изменений в технологическом и философском подходах к вебу. В этой статье мы расскажем все, что известно о данном явлении.
Что такое Web 3.0?
Web 3.0 это концепция эволюции интернета и веб-технологий, которая стремится изменить способ взаимодействия с онлайн-содержанием, данными и другими пользователями. Этот термин был введен для описания перехода от Web 2.0, ориентированного на социальные сети и интерактивность, к новому этапу развития к более децентрализованному интернету.
Web 3.0 вдохновляет инновации во многих областях, включая финансы, здравоохранение, образование и даже интернет вещей. Это означает, что в будущем мы можем ожидать более персонализированный и эффективный опыт в онлайне, где мы будем иметь больший контроль над своими данными и более смарт-взаимодействия в интернете. Персонализация в случае с Веб3 планирует быть невероятно большой. Как будто где-то есть крупная и очень развитая нейросеть, главная задача которой - сделать вашу жизнь в интернете более удобной. И все это не для избранных, а для каждого пользователя в сети.
Какие преимущества Web3 предлагает?
Ключевые преимущества, которые предлагает Web3:
- Децентрализация. Одним из главных преимуществ Web3 является децентрализация. Это означает, что контроль над данными и информацией будет распределен между участниками сети, а не сосредоточен в руках крупных корпораций, государств и так далее. Это обеспечи большую независимость и безопасность данных.
- Собственность данных. Web3 позволяет пользователям иметь полный контроль над своими данными и цифровыми активами. Вы можете решать, кому предоставить доступ к вашим данным и как они будут использоваться.
- Улучшенная безопасность. Блокчейн и криптография являются неотъемлемой частью Web3, обеспечивая высокий уровень безопасности и защиты от мошенничества и взломов.
- Отсутствие цензуры и доступность. Web3 создает более свободное и независимое онлайн-пространство, где информация доступна без цензуры и ограничений.
- Полная прозрачность. Все транзакции и операции, проводимые в Web3, обычно регистрируются в публичных блокчейнах, обеспечивая высокую степень прозрачности и верифицируемости.
- Инновации и новые бизнес-модели. Web3 способствует созданию новых бизнес-моделей и позволяет инноваторам разрабатывать новые продукты и услуги на основе децентрализованных технологий.
- Смарт-контракты и автономные организации. Web3 включает в себя смарт-контракты, которые автоматизируют и обеспечивают исполнение соглашений без посредников. Это может привести к более эффективным и прозрачным бизнес-процессам.
- Личная идентификация. Web3 может предоставить новые способы личной идентификации, которые защищают приватность и предотвращают злоупотребление данными.
Web3 обещает создать более открытое, свободное и безопасное интернет-пространство, которое придет к пользе пользователям, разработчикам и обществу в целом.
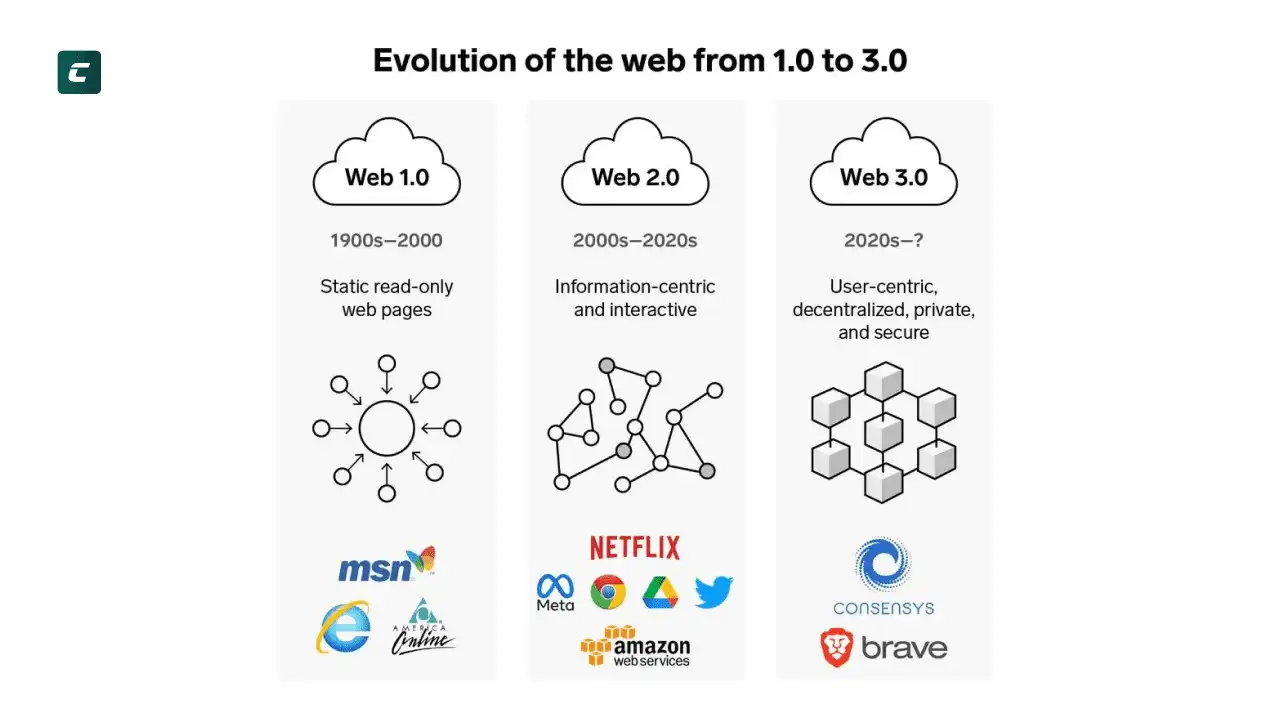
Web 1.0 (1989-2005)
Web 1.0, первое поколение интернета, охватывает период с конца 1980-х годов до примерно середины 2000-х. Этот этап интернета отличается от последующих поколений по своим характерным чертам и технологическим особенностям.
Основные черты Web 1.0 включают:
- Статические веб-сайты. Веб-страницы были в основном статичными, что означало, что они не менялись динамически в ответ на действия пользователя.
- Однонаправленная информация. Взаимодействие было ограничено. Пользователи могли просто просматривать содержание, но не вносить активный вклад.
- Низкое социальное взаимодействие. Популярные социальные сети, такие как Facebook и Х (Twitter), еще не существовали. Интернет был местом для потребления информации. Хотя уже существовали онлайн-форумы (первый был создан в 1979) и социальные сети (первая была создана в 1997), и даже всеми любимые Discord и Reddit, однако они не пользовались особой популярностью.
- Низкая скорость передачи данных. Скорость соединения была сравнительно низкой, что сильно ограничивало возможности для потоковой передачи мультимедийного контента.
- Отсутствие интерактивности. Интернет-приложения были ограничены, и возможности для онлайн-торговли, социальных сетей и интерактивных приложений были ограничены.
Web 1.0 был этапом, на котором интернет только начал проявлять свой потенциал как средство связи и информации. Это был временной отрезок, в котором были заложены основы для более интерактивного и социального интернета, который мы видим в последующих поколениях.

Web 2.0 (2005-настоящее время)
Web 2.0 представляет собой современное поколение интернета, которое началось примерно с середины 2000-х годов и продолжается в настоящем времени. Это поколение интернета отличается от предыдущего Web 1.0 по ряду ключевых аспектов, которые изменили способ взаимодействия с онлайн-пространством.
Основные характеристики Web 2.0 включают:
- Интерактивность и социальное взаимодействие. Web 2.0 предоставил возможность более активного взаимодействия пользователей. Социальные сети, блоги, форумы и веб-приложения позволяют пользователям создавать контент, обмениваться им и взаимодействовать друг с другом.
- Более динамичные веб-сайты. Веб-страницы стали более динамичными и интерактивными благодаря технологиям, таким как AJAX (асинхронный JavaScript и XML). Это позволило обновлять содержание на странице без полной перезагрузки.
- Облачные вычисления и хранилище. Внедрение облачных технологий позволило хранить и обменивать данные онлайн, обеспечивая доступ к ним с разных устройств.
- Расширение мобильных устройств. Распространение смартфонов и планшетов привело к возможности доступа к интернету в любое время и в любом месте.
- Аналитика и персонализация. Web 2.0 предоставил возможность анализа данных и персонализации контента, что позволяет предоставлять пользователям более релевантный опыт.
- Онлайн-сотрудничество и обмен знанием. Веб-приложения для совместной работы и обмена знанием, такие как Wikipedia и Google Docs, стали популярными.
Web 2.0 изменил способ, которым мы общаемся, работаем, развлекаемся и обмениваемся информацией. Это поколение интернета стало платформой для инноваций, создания новых бизнес-моделей и повсеместного социального взаимодействия.

Продукты Web 3.0: примеры и перечень
Web 3.0 привнес множество инновационных продуктов и платформ, которые отражают децентрализованный и инновационный характер этой эволюции интернета. Вот несколько примеров продуктов и сервисов, характерных для Web 3.0:
- Криптовалюты и криптокошельки. Bitcoin, Ethereum и другие криптовалюты представляют децентрализованные средства обмена и хранения активов. Криптокошельки позволяют пользователям управлять своими активами, совершать быстрые транзакции, обмены и другое. В целом ниша криптовалют широко развита и предлагает много новых технологий.
- Децентрализованные биржи. Платформы, такие как Uniswap и Dydx, предоставляют возможность обмена криптовалютами без посредников, что способствует и демонстрирует децентрализацию финансовых услуг.
- Смарт-контракты. Сеть Ethereum стала домом для смарт-контрактов и программ, которые автоматически исполняют соглашения без необходимости доверять третьей стороне.
- Децентрализованные приложения (DApps). DApps, такие как Decentraland, CryptoKitties и Golem, позволяют пользователям взаимодействовать и торговать без посредников.
- Децентрализованные хранилища данных. Проекты предоставляют децентрализованные методы хранения и обмена данными.
- Идентификация и авторизация. Продуктыпредоставляют децентрализованные решения для личной идентификации и авторизации.
- Децентрализованные организации (DAOs). DAOs позволяют участникам коллективно управлять организацией на основе смарт-контрактов.
- Web3-игры и развлечения. Децентрализованные игры, такие как Axie Infinity, предоставляют возможность заработка и взаимодействия в игровых мирах.
- Образование и знания. Проекты используют технологии блокчейна для улучшения доступа к образованию и знаниям.
- Финансовые продукты. DeFi (децентрализованные финансы) предоставляют доступ к кредитам, обмену и инвестированию без участия банков.
Эти продукты и сервисы представляют лишь малую часть многообразия инноваций, предложенных Web 3.0. Они позволяют пользователям более независимо управлять своими данными и активами, а также участвовать в экосистеме децентрализованных приложений и услуг. Рассмотрим все это более детально.
Децентрализованные финансовые (DeFi) платформы:
Децентрализованные финансовые (DeFi) платформы представляют собой инновационные финансовые сервисы, которые работают на базе блокчейн-технологий и устраняют необходимость в посредниках, таких как банки и биржи. Примеры популярных DeFi-платформ:
- Uniswap. Это децентрализованная биржа, которая позволяет пользователям обменивать различные криптовалюты и создавать ликвидность, получая за это вознаграждение.
- Compound. Платформа Compound предоставляет услуги по кредитованию и заимствованию криптовалюты, а также предлагает процентные ставки на депозиты.
- Aave. Это децентрализованная платформа для кредитования и заимствования, которая предоставляет пользователям доступ к множеству криптовалют.
- MakerDAO. Эта платформа предоставляет стабильную монету DAI, которая является криптовалютой, привязанной к доллару США, и использует систему голосования для управления стабильностью цены.
- Yearn.webp. Yearn.Finance создает автоматизированные стратегии для максимизации доходности в DeFi, обеспечивая оптимальное размещение средств.
Эти платформы предоставляют широкий спектр финансовых услуг, такие как обмен, кредитование и инвестирование, и позволяют пользователям управлять своими активами без посредников. Однако важно помнить о рисках, связанных с вложениями в DeFi, и о том, что они могут подвергаться воздействию рыночных колебаний.
Распределенные хранилища данных
Распределенные хранилища данных представляют собой инновационные решения для хранения и обмена данными, которые строятся на базе технологии блокчейн и децентрализации. Они обеспечивают улучшенную безопасность и доступность данных. Некоторые примеры распределенных хранилищ данных включают:
- InterPlanetary File System (IPFS). IPFS - это протокол и сеть для хранения и обмена файлами. Он разбивает файлы на блоки и распределяет их по сети, обеспечивая быстрый доступ и устойчивость к сбоям.
- Filecoin. Этот проект использует IPFS и блокчейн для создания децентрализованного рынка хранилища данных. Пользователи могут арендовать место на компьютерах других пользователей и получать за это вознаграждение.
- Storj. Storj - это платформа для хранения и обмена файлами, построенная на технологии блокчейн. Она использует децентрализованные узлы хранения данных, чтобы обеспечить безопасное и эффективное хранение файлов.
- Sia. Sia - это децентрализованная платформа для хранения данных, которая позволяет пользователям сдавать в аренду свободное место на своих жестких дисках и получать за это криптовалюту.
Эти распределенные хранилища данных предоставляют улучшенную безопасность, доступность и контроль над данными пользователями, и они становятся все более популярными в контексте Web 3.0, который призывает к децентрализации и защите данных.
Контент на основе блокчейна
Контент на основе блокчейна представляет собой контент, создаваемый и управляемый с использованием технологии блокчейн. Эта технология обеспечивает прозрачность, авторское право и цифровую уникальность контента. Некоторые примеры контента на основе блокчейна включают:
- NFT (невзаимозаменяемые токены). NFT это цифровые активы, которые используются для представления уникальных и невзаимозаменяемых предметов, таких как цифровые произведения искусства.
- Музыка и аудио. Артисты и музыканты могут выпускать свои песни и альбомы в виде NFT, обеспечивая правильное вознаграждение и авторские права.
- Игры. Компании разрабатывают игровые предметы и персонажей, которые можно купить и продать с использованием NFT, придавая им уникальную ценность.
- Издательства и журналистика. Некоторые издательства используют блокчейн для подтверждения подлинности новостных статей и исследовательских работ.
- Образовательный контент. Платформы на основе блокчейна предоставляют образовательные материалы и сертификаты, гарантируя их подлинность.
Этот контент обеспечивает доверие и прозрачность в онлайн-среде, а также предоставляет новые возможности для монетизации и распространения цифровых активов.
Умные контракты
Умные контракты - это программные соглашения, выполнение которых автоматизировано с использованием блокчейн-технологии. Они предоставляют безопасный и децентрализованный способ заключения и выполнения контрактов. Некоторые примеры использования умных контрактов включают:
- Инвестиции и финансы. Умные контракты могут автоматически выплачивать проценты или дивиденды инвесторам на основе условий контракта.
- Страхование. Умные контракты могут автоматически выплачивать страховое возмещение при наступлении определенных событий, таких как стихийные бедствия.
- Недвижимость. Умные контракты могут упростить процесс покупки и продажи недвижимости, автоматизируя перевод средств и передачу прав собственности.
- Логистика и поставки. Умные контракты могут отслеживать поставки и автоматически выплачивать платежи поставщикам при выполнении условий контракта.
- Образование и академия. Умные контракты могут автоматически управлять академическими записями, сертификатами и платежами для обучения.
- Социальные соглашения. Умные контракты могут упростить создание и выполнение соглашений между сторонами, такие как брачные договоры и наследство.
Эти примеры демонстрируют многообразие областей, где умные контракты могут быть полезными для автоматизации и упрощения процессов. Они позволяют участникам контракта доверять автоматическому исполнению без посредников.
Виртуальная реальность (VR) и расширенная реальность (AR):
Виртуальная реальность (VR) и расширенная реальность (AR) представляют собой передовые технологии, меняющие способ взаимодействия с окружающим миром и создания цифровых сценариев.
Виртуальная реальность (VR) погружает пользователя в полностью виртуальное окружение, отделяя его от реального мира. Примеры VR включают в себя игры и симуляторы, обучение и тренинги, а также виртуальные музеи и культурные мероприятия.
Расширенная реальность (AR) добавляет цифровые элементы в реальное окружение пользователя. Примеры AR включают мобильные приложения, которые позволяют видеть информацию о местах или продуктах через камеру смартфона, а также AR-очки, которые добавляют интерактивные элементы вокруг вас.
Обе технологии используются в различных сферах, включая игры, образование, медицину, дизайн, маркетинг и многое другое. VR и AR продолжают развиваться и изменять способ взаимодействия с цифровым и реальным миром.
Машинное обучение и искусственный интеллект
Машинное обучение и искусственный интеллект (ИИ) играют важную роль в контексте Web3, привнося инновации и усовершенствования в децентрализованные приложения и сервисы. Эти технологии могут обеспечивать автоматизацию и улучшенные возможности анализа данных. Примеры включают:
- Улучшенные рекомендации. ИИ используется для анализа предпочтений пользователей и предоставления персонализированных рекомендаций, как в сфере контента, так и в финансовых услугах.
- Автоматизированный анализ данных. Машинное обучение помогает в анализе больших объемов данных на основе смарт-контрактов и блокчейнов, что позволяет легче выявлять тренды и аномалии.
- Интеллектуальные контракты. Умные контракты могут использовать ИИ для принятия более сложных решений на основе данных, учебных моделей и алгоритмов.
- Искусственный интеллект для креативности. ИИ может быть использован в сферах искусства и геймдизайна, создавая уникальные и интересные визуальные и аудиоэффекты.
- Обучение на основе данных блокчейна. Исследователи могут использовать множество данных, собранных с блокчейна, для обучения моделей машинного обучения и предсказания рыночных трендов.
ИИ и машинное обучение дополняют децентрализованные технологии в Web3, обогащая их функциональность и обеспечивая новые возможности для улучшения процессов и взаимодействия с данными.
Как Web 3.0 влияет на будущее Интернета?
Web 3.0, также известный как "семантический веб," имеет потенциал радикально изменить будущее Интернета, делая его более интеллектуальным, децентрализованным и интерактивным. Этот переход в новую эпоху означает более глубокое понимание и взаимодействие данных в сети, что может повлиять на множество сфер, включая поиск информации, социальные медиа, финансы и медицину.
Одной из ключевых характеристик Web 3.0 является создание семантических связей между данными, что позволит поисковым системам и приложениям более точно понимать контекст запросов. Это позволит более точно отвечать на вопросы пользователей и предоставлять релевантную информацию.
Вот что об этом думают некоторые известные личности:
- Тим Бернерс-Ли, создатель Всемирной паутины: "Web 3.0 - это идея о более умном вебе, где информация более четко структурирована, и мы способны создавать связи между данными."
- Сергей Брин, сооснователь Google: "Web 3.0 будет означать больше индивидуализации, более точного поиска и, возможно, даже более децентрализованную структуру."
- Джек Дорси, сооснователь Twitter и Square: "Web 3.0 может привести к более прозрачной и децентрализованной системе обмена информацией и ценностями."
Эти цитаты подчеркивают значимость Web 3.0 в будущем Интернета, предсказывая более интеллектуальное и децентрализованное будущее, в котором данные и информация станут более доступными и понятными для пользователей.
Критика в отношении Web 3
Web 3.0, как перспективное направление в развитии Интернета, не лишено критики. Некоторые известные личности и эксперты высказывают опасения и сомнения относительно этой концепции. Критика может быть связана с проблемами безопасности, концентрацией власти и другими аспектами. Вот несколько ключевых моментов критики Web 3.0:
- Безопасность и приватность. Системы Web 3.0 могут быть уязвимыми для новых видов кибератак и злоупотреблений. Это вызывает опасения относительно безопасности личных данных и финансовых транзакций.
- Децентрализация vs. централизация. Некоторые опасаются, что Web 3.0 может привести к новым формам централизации, особенно в области блокчейна и криптовалют.
- Сложность использования. Для обычных пользователей некоторые аспекты Web 3.0 могут быть слишком сложными, что может стать барьером для массового принятия.
- Экологические аспекты. Процессы добычи криптовалют и многие технологии Web 3.0 могут быть негативными с точки зрения экологии, что вызывает обеспокоенность относительно устойчивости их развития.
Вот что говорят критики:
- Виталик Бутерин, сооснователь Ethereum: "Web 3.0 - это чудесная идея, но нам нужно уделять особое внимание безопасности и защите данных, чтобы избежать серьезных уязвимостей."
- Тим Бернерс-Ли, создатель Всемирной паутины: "Web 3.0 - это потенциально красивое будущее, но мы должны бороться за децентрализацию и прозрачность, чтобы избежать новых форм централизации."
- Экологические активисты. Многие экологические группы и личности выражают обеспокоенность из-за потенциальных экологических последствий массового использования криптовалют и технологий Web 3.0.
Критика Web 3.0 служит напоминанием о важности развивать эту концепцию с учетом безопасности, прозрачности и экологической устойчивости, чтобы она могла реализовать свой полный потенциал.
Мнение у команды Cryptology KEY относительно Web 3.0
Не идти в ногу со временем - это ошибка, ведь процесс развития технологий только ускоряется.
Такую ошибку уже допустило старшее поколение, которое "на Вы" с современными телефонами и другими технологиями.
Сейчас мы видим быструю интеграцию новых решений, которые упрощают и улучшают наши жизни. Важно не отставать и погружать в происходящее, иначе вы рискуете быть ненужными специалистами или быть лишёнными всех блага современных технологий.
Что такое Web 3.0?
Какие технологии играют ключевую роль в Web 3.0?
Как Web 3.0 влияет на конфиденциальность данных?
Какие примеры использования Web3 в реальной жизни?
Какие преимущества предоставляет Web3 пользователям?

Тогда расскажи друзьям – пусть тоже прокачивают свои навыки. Поделиться можно легко с помощью кнопок внизу или просто скопировав ссылку. Мы будем рады твоим отметкам в соц. сетях!
Поделиться

Подписывайся на нашу email-рассылку и получай свежие аналитические обзоры, новости, инсайты и приглашения на прямые эфиры прямо в свой почтовый ящик. Никакого спама — только ценная информация для трейдеров!










