Что такое японские свечи

Мышление богатых

Финансовая грамотность: что это такое и как стать финансово грамотным

Что из себя представляет плановая экономика?
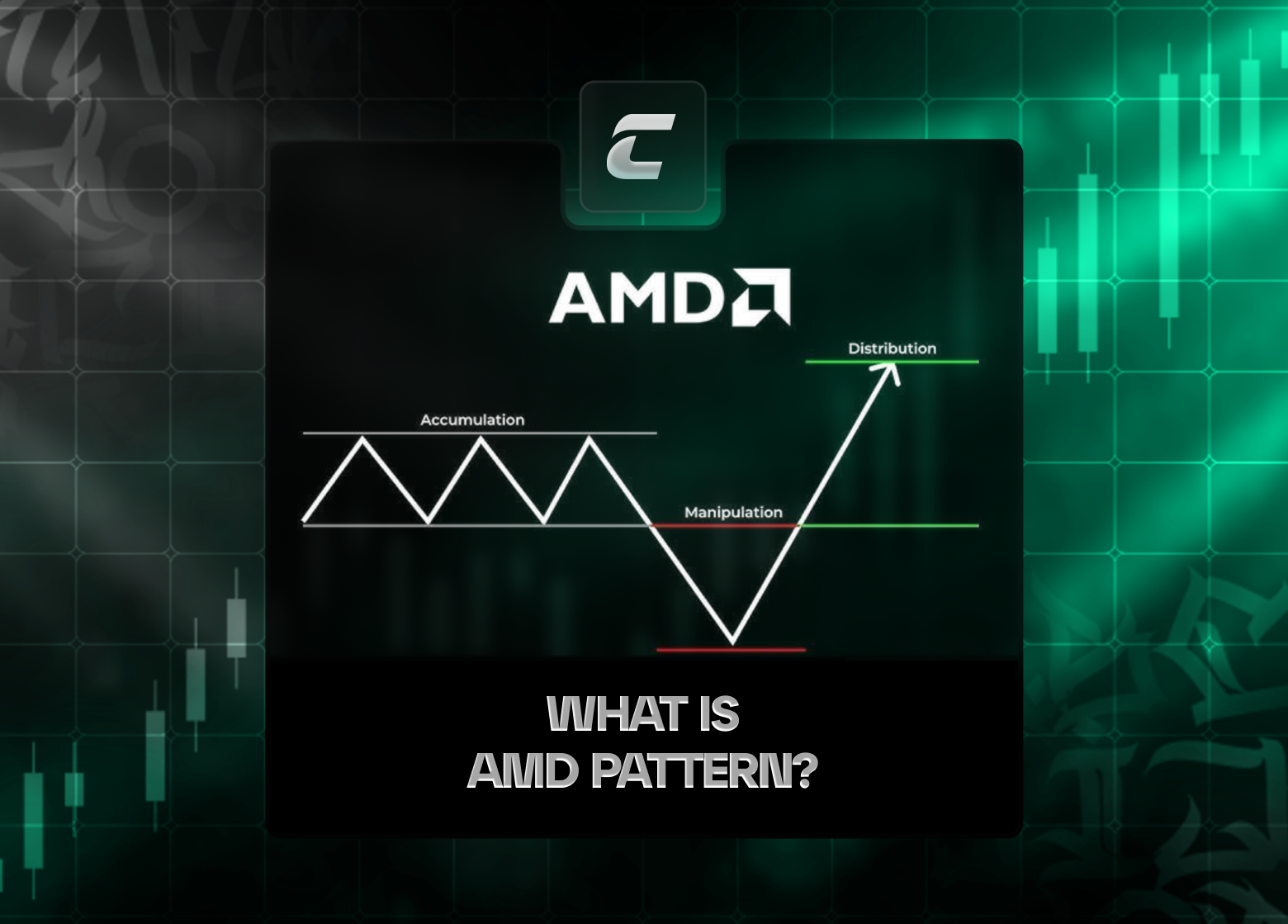
Что такое AMD?

РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ WORKSHOP V.9
Недельный план - 13.01 - 17.01.2025

Что такое SocialFI?

Что такое Fed rate?

Что привело к появлению криптовалют?

2024 Recap: подводим итоги, смотрим на результаты и строим новые цели
Недельный план - 23.12 - 27.12.2024




