Последние статьи

Что такое марксизм?

Что такое монополия?

Что такое макроэкономика

Что такое майнинг-пул (mining pool) и как он работает

Что такое инвестиционный портфель и зачем его собирать?
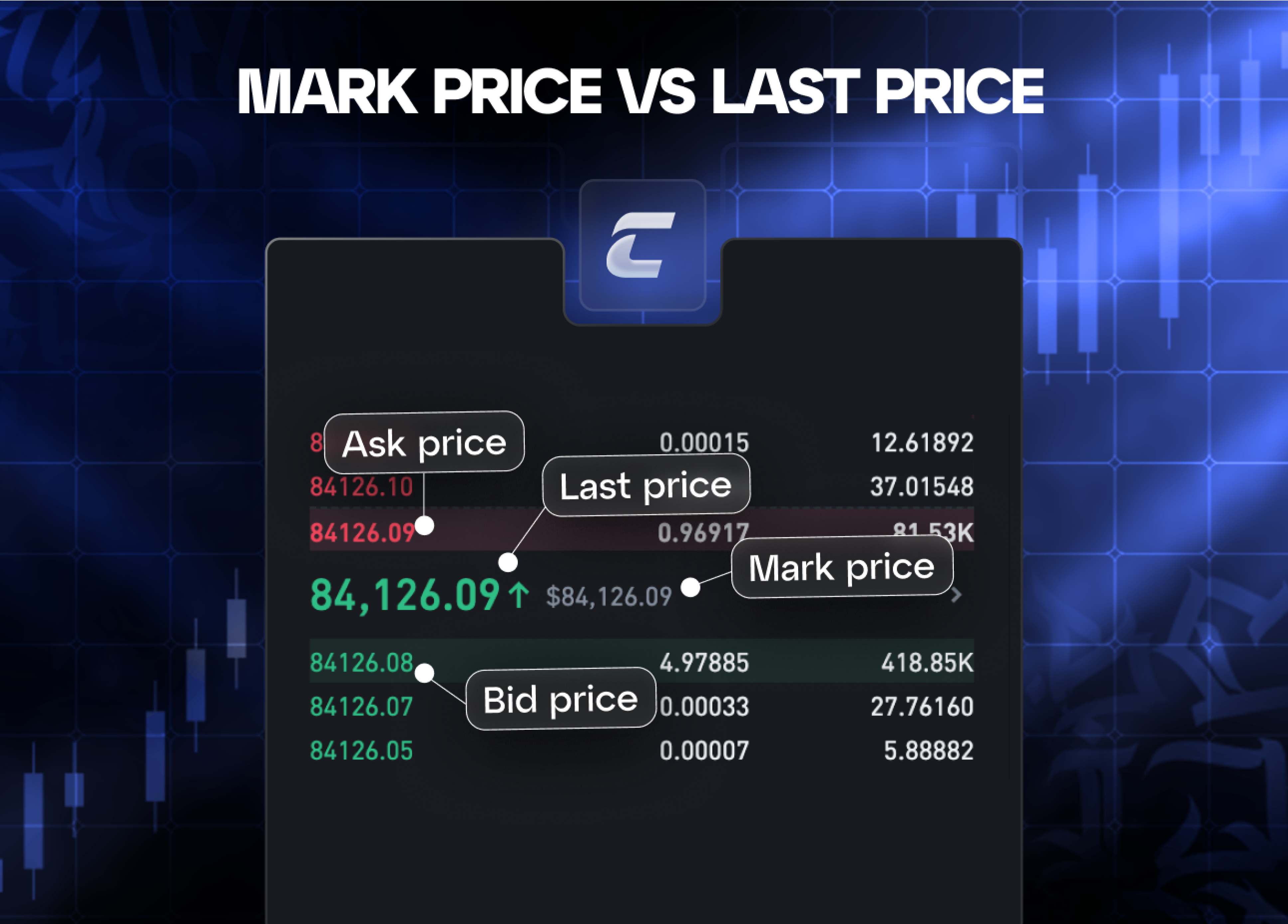
В чем разница между ценой маркировки и последней ценой?

Результаты Workshop V10
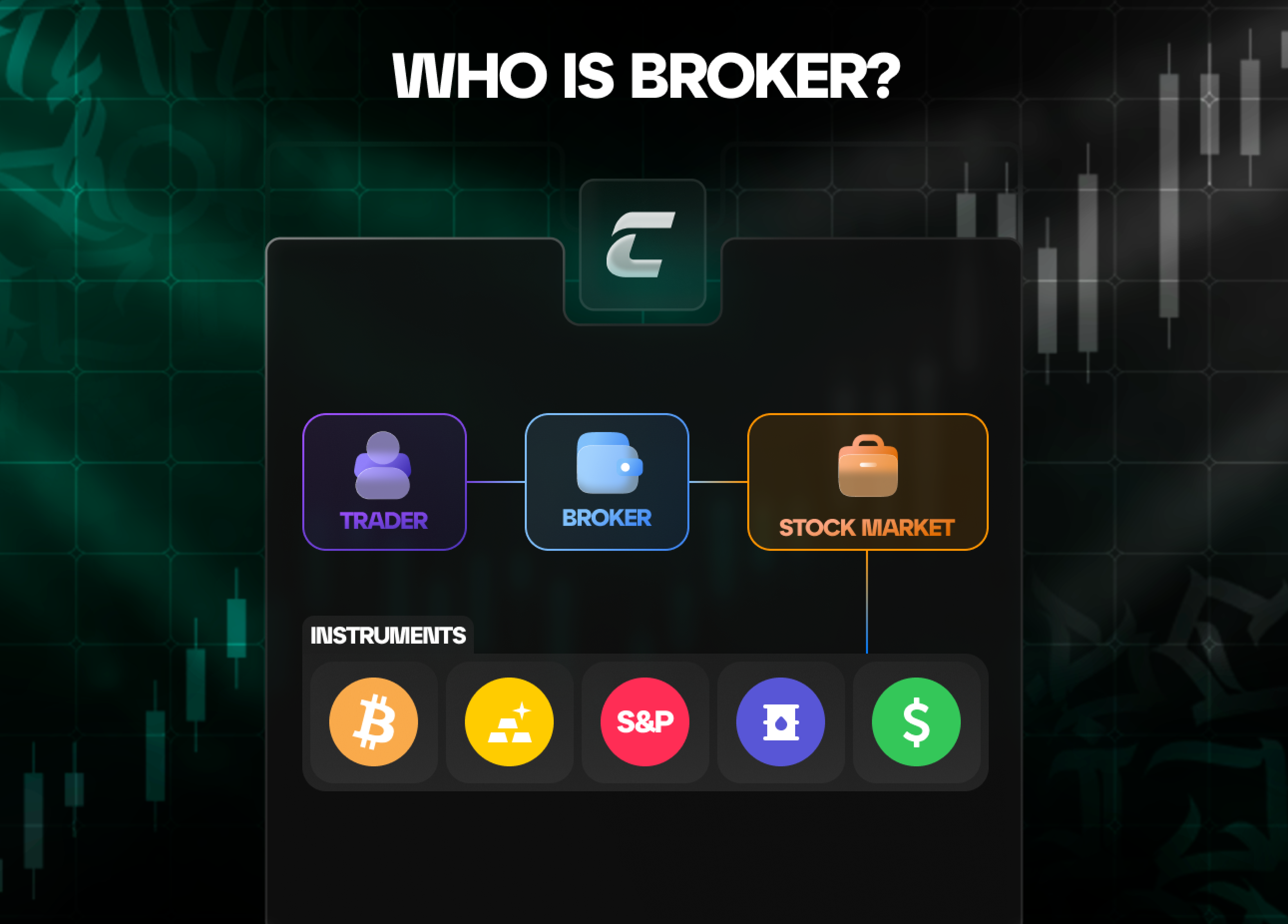
Кто такой брокер

Крипто робот - типы и как на них зарабатывать

Можно ли совмещать торговлю и основную работу

Что такое AI-агенты в криптовалюте?
Индикаторы технического анализа: назначение и роль в трейдинге


