Что такое сеть?
Для криптосферы, сетью является блокчейн. Существует большое количество определений, по разному описывающих данную технологию. Если максимально обобщить, то сеть - это цифровое пространство, распределенное между узлами (нодами) сети, позволяющее осуществлять работу с максимальным доверием к данным.
Это пространство может использоваться в различных целях: транзакции, вычисления, хранение данных и т.д.
Долгое время концепция децентрализации обсуждалась небольшим кругом криптографов. В академических кругах велась активная работа по созданию технологий, способных воплотить ее в жизнь.
Очень часто технологии появляются раньше, чем создается запрос от массового пользователя. Кризис 2008 года и ответные меры центробанков по эмиссии новых денег, заставили людей задуматься о рисках чрезмерной централизации власти.
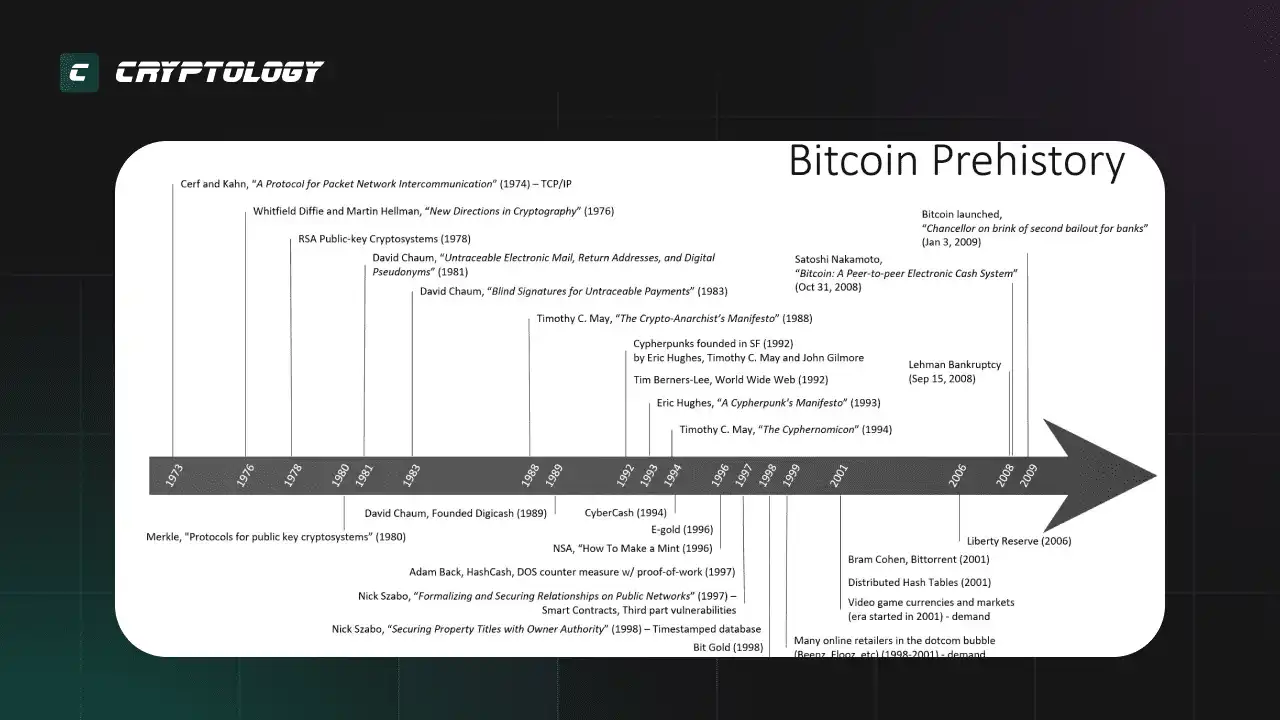
В ответ на это была создана первая криптосеть - Bitcoin, задачей которой было создание децентрализованной платежной системы.
Популярность Bitcoin активно росла, активные пользователи и энтузиасты начали задумываться о более широком применении технологии.
Самая популярная сеть Ethereum
Как было отмечено выше, технология впервые была использована для создания платежной системы, но Виталик Бутерин и его коллеги пошли дальше и предложили создать сеть, на которой можно было бы запускать смарт-контракты (программы).
Начался взрывной рост, повлекший за собой появление различных криптосегментов.
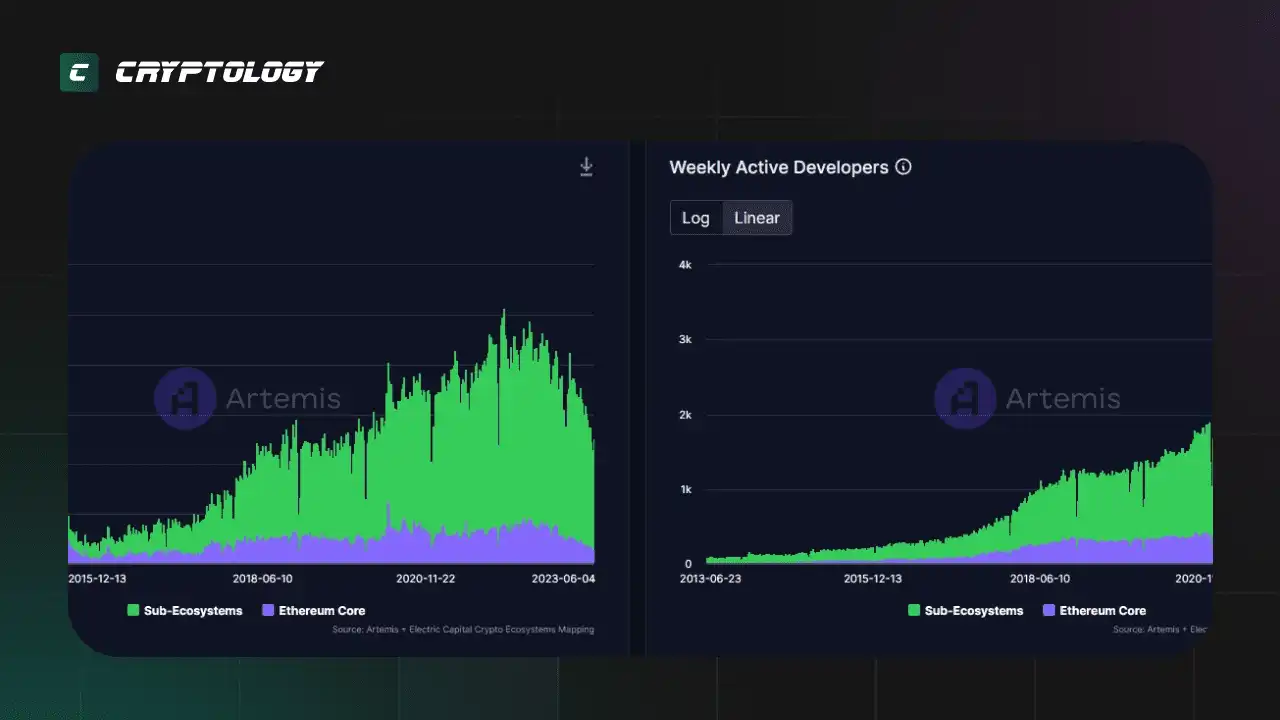
Токенов в сети Ethereum становилось все больше, появилась проблема со совместимостью, так как как они использовали отдельные смарт-контракты.
Для упрощения жизни разработчиков, команда Ethereum решила унифицировать правила для развертывания токенов. 19 ноября 2015 года, Виталик Бутерин и Фабиан Фогельштеллер опубликовали новый стандарт ERC-20.
Это еще больше усилило рост проектов, так как они смогли упростить разработку.
1275 основных токенов созданных на базе стандарта ERC-20.
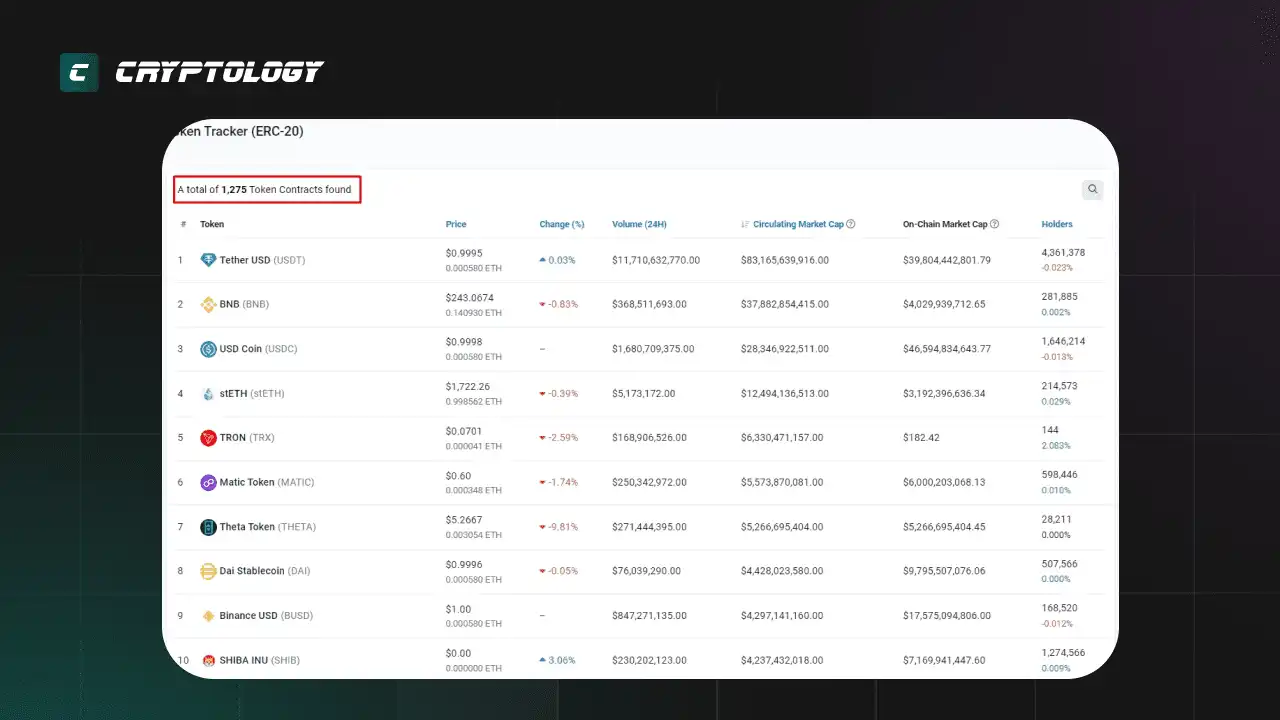
Разработка технического стандарта ERC-20
С того момента рынок продолжал развиваться, появились новые подходы в работе с токенами, что повлекло за собой создание новых технических стандартов в сети Ethereum.
- ERC-721 - отец NFT. С помощью данного стандарта создается любое NFT.
- ERC-777 - позволяет создавать дополнительные функции поверх токенов. Например, повышение конфиденциальности транзакций или аварийное восстановление, чтобы выручить вас, если вы потеряете свои закрытые ключи. Из-за определенных технических проблем, распространение не получил.
- ERC-1155 - позволяет повысить эффективность переводов путем объединения транзакций, тем самым снижая затраты. Также позволяет объединять NFT и взаимозаменяемые токены в виде одного токена.
- ERC-4626 - стандарт токенизированного хранилища, предназначенный для оптимизации и унификации технических параметров доходных хранилищ в DeFi.
- И много других.
Обозреватель (эксплорер) сети Ethereum - https://etherscan.io/.
Зачем столько стандартов спросите вы. Сфера постоянно развивается, появляются новые идеи, что заставляет придумывать решения для их реализации. Именно поэтому, для упрощения работы постоянно появляются новые технические стандарты.
Из-за базовых ограничений, которые имеет сеть Ethereum, многие проекты выпустили видоизмененные копии Ethereum решающие эти проблемы (масштабируемость, скорость). Стандарты токенов и принципы работы остались одинаковыми, поэтому Ethereum и новые системы взаимосвязаны. Проекты улучшили недостатки описанные выше, а также взяли преимущества - разработчиков, комьюнити, объемы и так далее.
Поддерживается сетью BNB Chain. Проект пошел по пути улучшения и оптимизации недостатков Ethereum. Дешевые комиссии, быстрая скорость, упрощенная среда разработки. К большому сожалению пришлось пожертвовать децентрализацией.
BNB Chain лидирует по количеству активных пользователей среди всех сетей, однако отстает от Ethereum по объему транзакций, количеству активных разработчиков и проектов.
1208 основных токенов созданных на базе стандарта BEP-20 из 3,4 миллионов токенов.
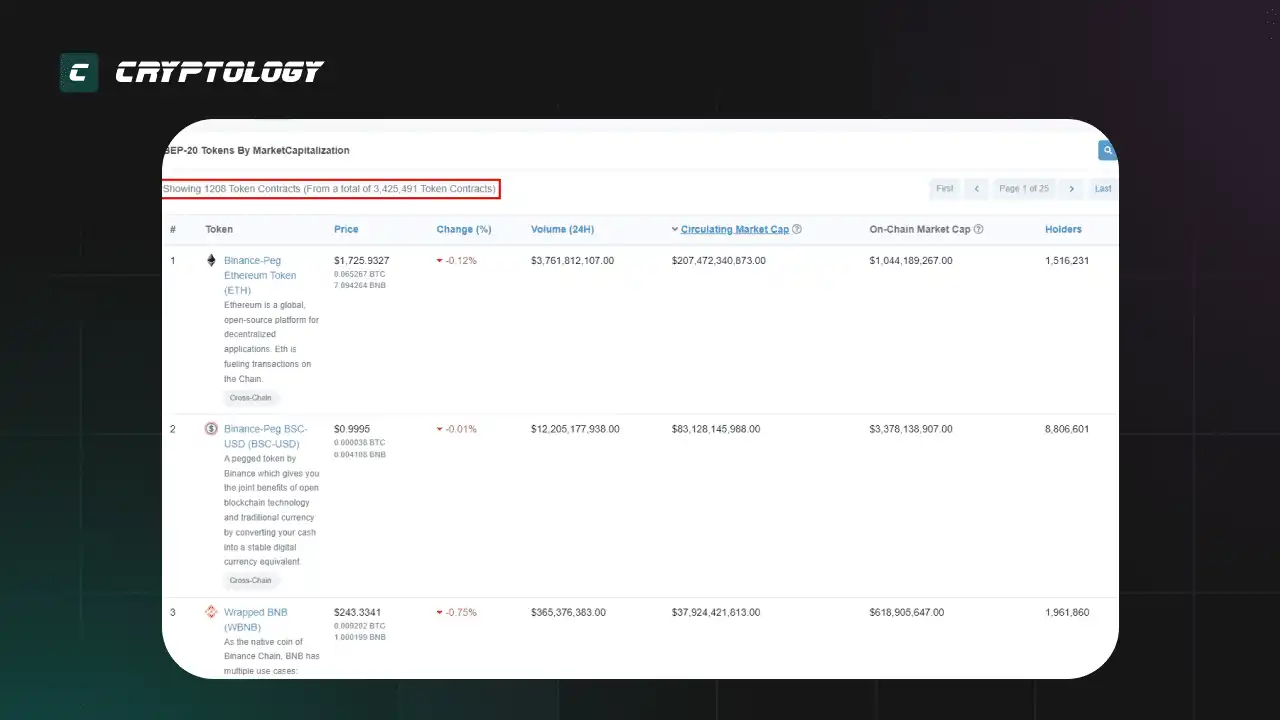
Технический стандарт BEP-20
Поддерживается сетью BNB Chain. Проект пошел по пути улучшения и оптимизации недостатков Ethereum. Дешевые комиссии, быстрая скорость, упрощенная среда разработки. К большому сожалению пришлось пожертвовать децентрализацией.
BNB Chain лидирует по количеству активных пользователей среди всех сетей, однако отстает от Ethereum по объему транзакций, количеству активных разработчиков и проектов.
1208 основных токенов созданных на базе стандарта BEP-20 из 3,4 миллионов токенов.
BNB Chain также перенял многие технические стандарты от сети Ethereum.
- BEP-20 - это стандарт токенов в сети BNB Chain, расширяющий функционал стандарта ERC-20.
- BEP-721 - аналог ERC-721, применяется для операций с NFT.
Обозреватель (эксплорер) сети BNB Chain - https://bscscan.com/.
Поддерживается сетью Tron. Проект пошел такой же дорогой, как и BNB Chain - увеличение скорости транзакций, удешевление комиссий. Однако у Tron не получилось создать серьезного конкурента для Ethereum или BNB Chain. Основное использование данной сети - переводы токена USDT, который активно используют пользователи.
77710 токенов созданных на базе стандарта TRC-20.
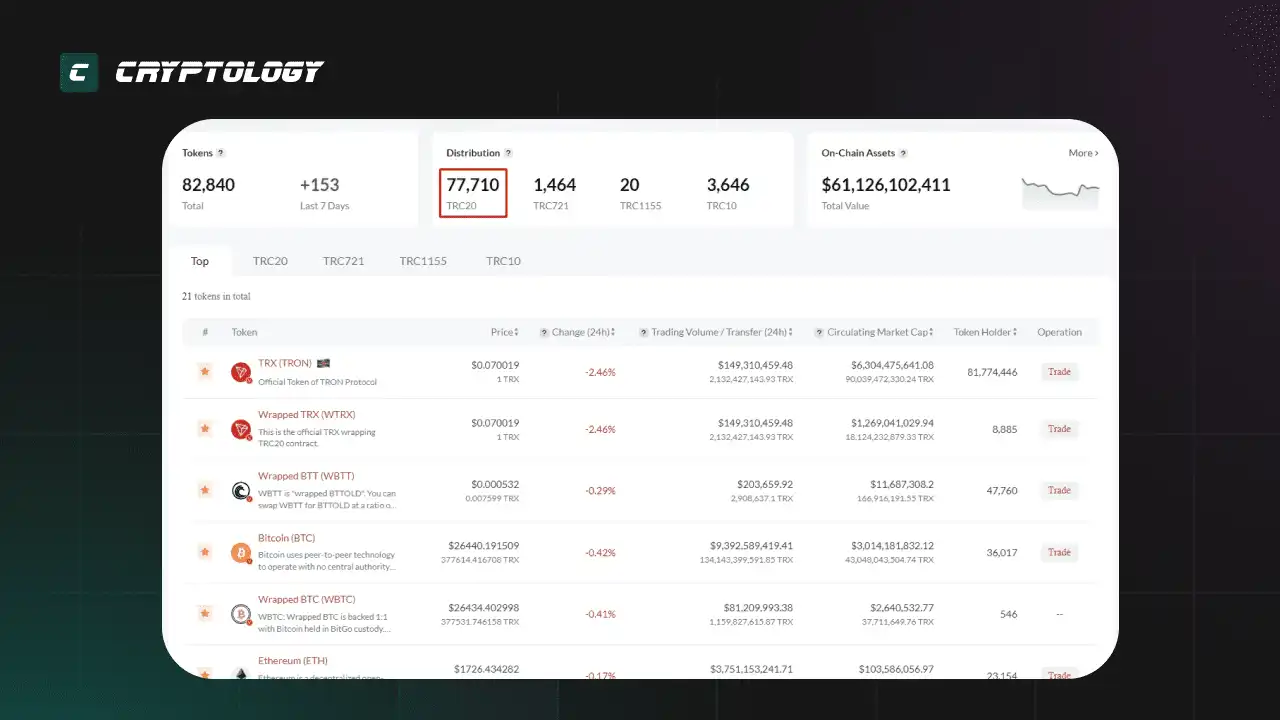
Технический стандарт TRC-20
Работая на основе Ethereum, Tron также перенял многие технические стандарты.
TRC-10 - базовый стандарт токенов блокчейна Tron.
TRC-20 - стандарт использующийся для создания смарт-контрактов.
TRC-721 - стандарт для работы с NFT.
TRC-1155 - позволяет повысить эффективность переводов путем объединения транзакций, тем самым снижая затраты.
Обозреватель (эксплорер) сети Tron.
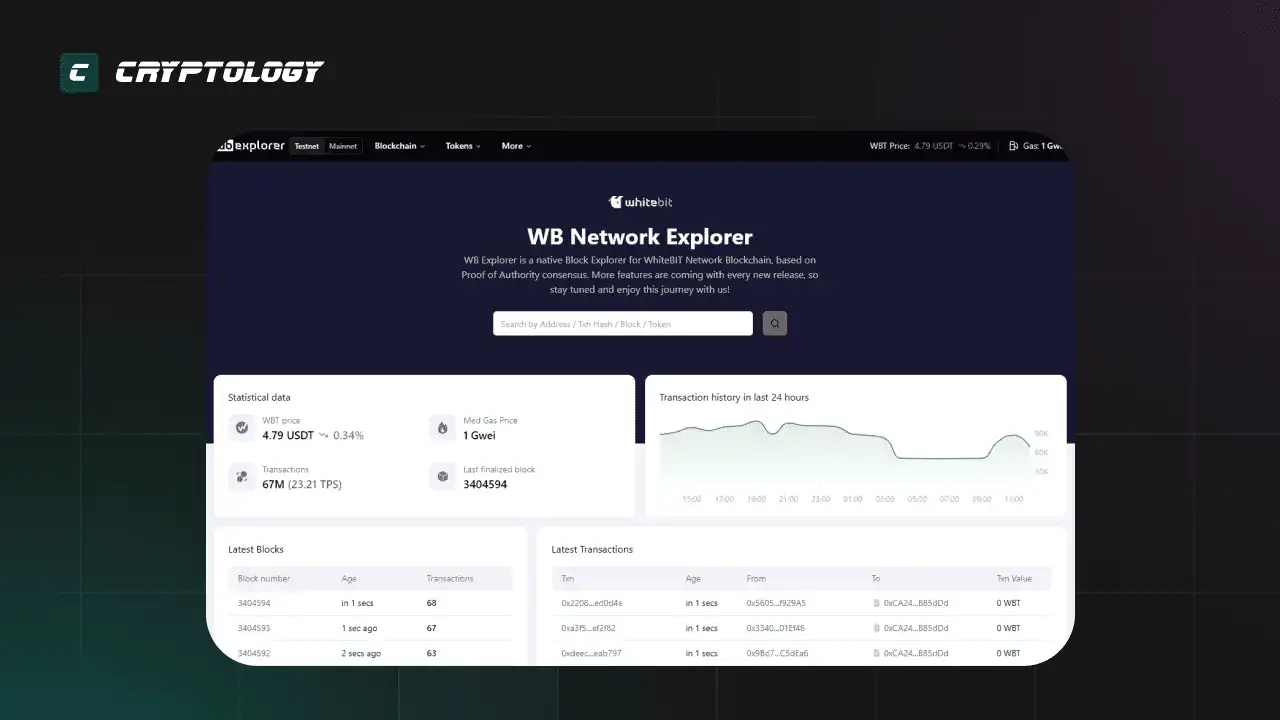
Біржа WhiteBIT запускає свій блокчейн WB Network для розміщення як власних, так і сторонніх проектів. Наразі він проходить тестування, в якому може взяти участь кожен охочий.
Активна розробка та впровадження нових сервісів приваблює велику кількість користувачів, що забезпечить прийняття нової екосистеми.
7478 тестових токенів, створених на основі стандарту WRC-20.
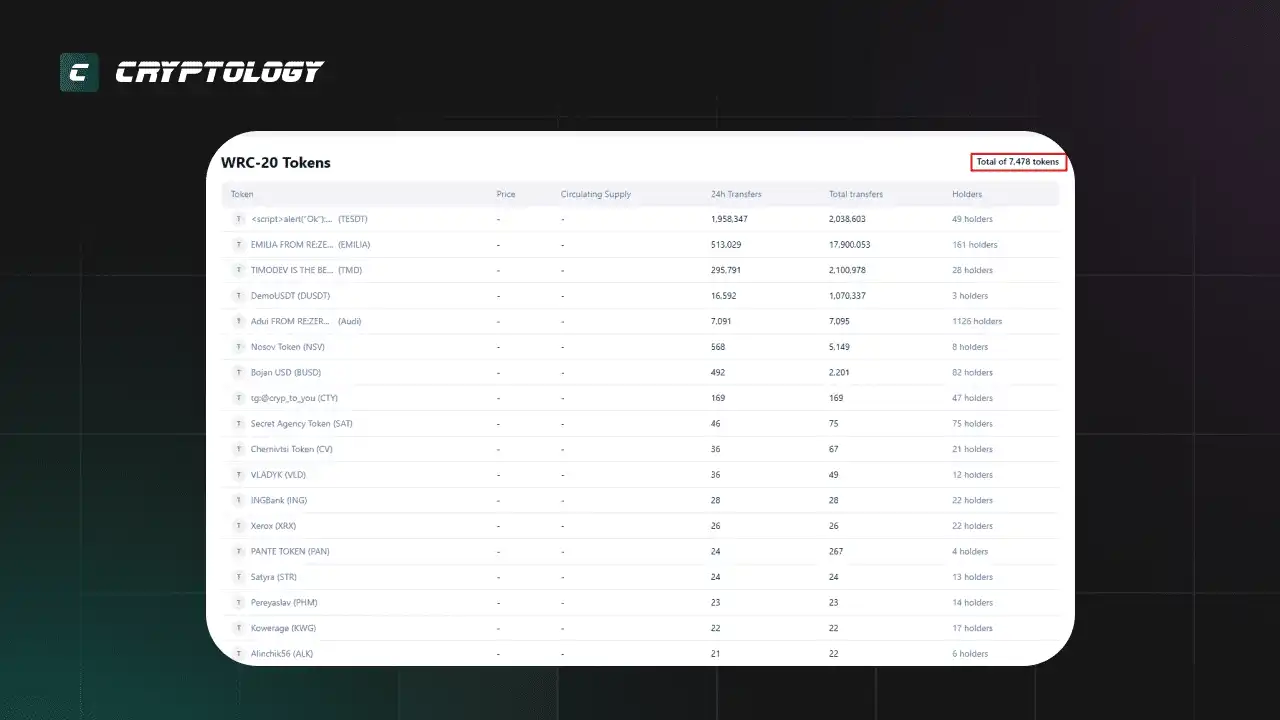
Технический стандарт WRC-20
Вероятнее всего WB Network позаимствует основные технические стандарты блокчейна Ethereum.
WRC-20 - стандарт использующийся для создания смарт-контрактов.
WRC-721 - стандарт для работы с NFT.
Обозреватель (эксплорер) сети WB Network.
Что такое стандарт ERC-20?
Какие основные функции предоставляет стандарт ERC-20?
Что такое стандарт BEP-20?
Какие преимущества у стандарта BEP-20?
Что такое стандарт TRC-20?
Какие преимущества у стандарта TRC-20?
Что такое стандарт WRC-20?
Какие преимущества у стандарта WRC-20?

Тогда расскажи друзьям – пусть тоже прокачивают свои навыки. Поделиться можно легко с помощью кнопок внизу или просто скопировав ссылку. Мы будем рады твоим отметкам в соц. сетях!
Поделиться

Подписывайся на нашу email-рассылку и получай свежие аналитические обзоры, новости, инсайты и приглашения на прямые эфиры прямо в свой почтовый ящик. Никакого спама — только ценная информация для трейдеров!