Последние статьи

Что такое шорт-сквиз и как он работает

Как пользоваться Ledger: полный гайд: как пользоваться Ledger

Что такое WhitePaper
Бинарные опционы: что это такое и как они работают

Как найти и восстановить потерянный Биткоин-кошелек
Что такое котировка
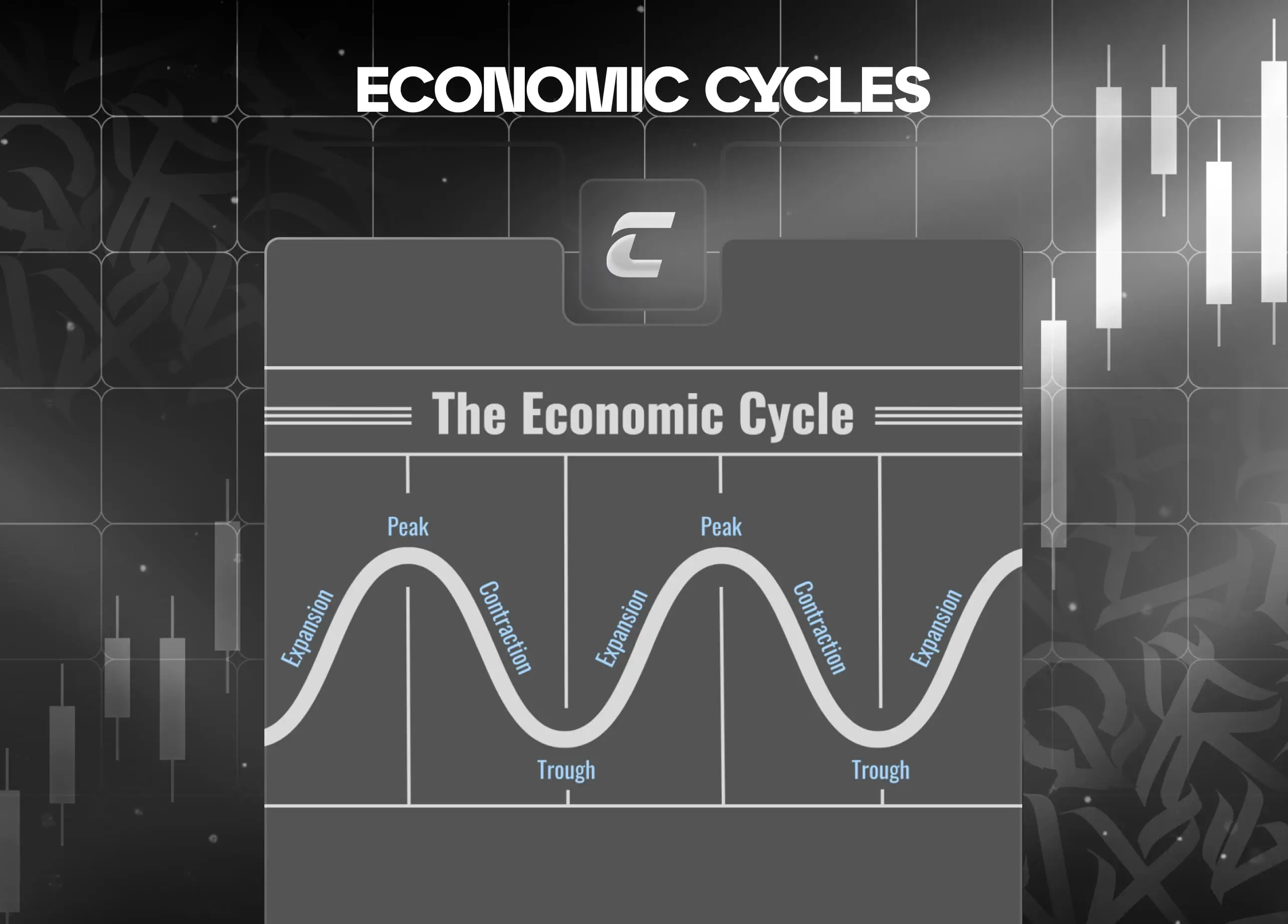
Что такое экономические циклы: фаза роста, пика, спада и восстановления

Как бороться с тревожностью во время открытой позиции

Ожидание быстрого результата: главный враг трейдера-новичка

Как пережить затяжную серию убыточных сделок

Отзыв студента: Сергей об обучении в Cryptology Key

Что такое теневая экономика и почему она мешает росту страны

